Standardisation versus adaptation issues in International Marketing (2004)
What differentiates the proponents of standardisation from the proponents of adaptation is how homogenous they perceive consumers and markets across different countries to be. On one side, the proponents of standardisation believe that the markets and consumer needs and wants around the world are converging or homogenising as a result of globalisation, to the extent that the same marketing programme can be used across all countries.
On the other, the proponents of the adaptation approach believe that, despite the converging forces of globalisation, markets as well as consumer needs and wants will remain heterogeneous across the world, calling for adaptation across countries. The dissertation will commence with a review of the literature concerned with the standardisation versus adaptation debate in international marketing, placing specific emphasis on the debate within the setting of the EU and the extent to which the debate has incorporated services.
The next chapter focuses on the research framework, developing a theoretical foundation from which the findings of the empirical research will be analysed. After a chapter dedicated to the outline of the research methodology of the study, the similarities and differences in the preferences of British and German consumers regarding the marketing communications of mobile telecommunication service providers and the marketing communication tools and techniques used by O 2 and T-Mobile in the UK and Germany are compared in the results chapter.
Following this will be a chapter devoted to the discussion of the results determining whether the preferences of British and German respondents to the survey can be related to the characteristics of the British and German national cultures, highlighting whether the standardisation or adaptation of marketing communications of O 2 and T-Mobile in practice correspond to the degree of standardisation or adaptation the service provider claims to be using and whether the marketing communication tools and techniques match the preferences of consumers, analysing the results of the study in terms of their relation to previous research findings and finally outlining the limitations of the study. The study will be concluded with a review of the findings and suggestions for future research.
- 15,000 words – 74 pages in length
- Excellent use of literature
- Good analysis of subject area
- Well written throughout
- Includes questionnaire
- Ideal for marketing students
1: Introduction
Standardisation versus adaptation debate
Standardisation versus adaptation debate in the European Union
Standardisation versus adaptation debate for services
Mobile telecommunication industry
Focus of the investigation
Outline of the study
2: Literature Review
International marketing
Culture
Elements of culture
The challenges of international marketing
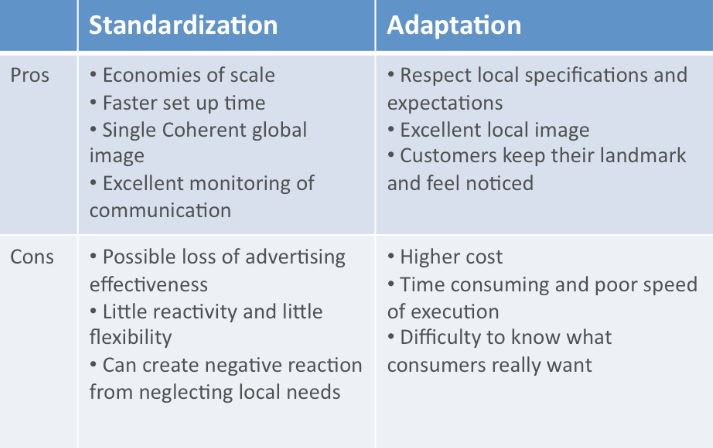
Standardisation versus adaptation debate in international marketing
Standardisation
Adaptation
The trade-off
An unnecessarily polarised debate?
The influence of globalisation
Increasing integration and convergence in the European Union
The European Union and cultural differences
Services – a neglected area of the debate
International trade of services
International marketing of services
Marketing communications
Communication processes
Importance of marketing communications
Marketing communications for services
Marketing communications mix
Integrated marketing communications
Marketing communications and culture
Research objectives
3: Research Framework
Hofstede’s dimensions of culture
Rankings of the United Kingdom and Germany
Hall’s cultural dimensions
Rankings of the United Kingdom and Germany
Hall’s cultural dimensions in a marketing context
Limitations of cultural frameworks
Conclusion
4: Research Methodology
Consumer preferences of marketing communications
Data collection instrument
Sampling
Questionnaire design
Construct development
Translation
Pilot testing
Statistical testing
The marketing communications of T-Mobile and O2
5: Data Analysis
Survey results
Sample Characteristics
Consumer preferences
Total sample responses
Comparison of British and German responses
Analysis of marketing communications of T-Mobile and O2
Marketing communications of O2
Marketing communications of T-Mobile
Conclusion
Summary
6: Discussion
Preferences and cultural characteristics
Power distance
Masculinity
Individualism
Uncertainty avoidance
High versus low context
Summary
O2 and T-Mobile marketing communications versus consumer preferences
Marketing communication tools
Marketing communication techniques
Summary
Standardisation versus adaptation in practice
Relation to research dedicated to international service marketing communications
Relation to research dedicated to pan-European marketing
Implications of findings for standardisation versus adaptation theory
Standardisation versus adaptation – the future
Limitations
7: Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusions
Recommendations for future research
References
Appendix Section
Questionnaire